Athlete's Foot - Infections, Care, Contagious, Definition (Skin)
Definition Athlete's Foot
Athlete's foot is a very common skin infection of the feet caused by fungus. The fungus that commonly causes athlete's foot is called Trichophyton. When the legs or other areas of the body stay moist, warm, and irritated, this fungus can grow and infect the upper layer of the skin. Fungal infections can occur anywhere on the body, including the scalp, body, body, limbs (arms and legs), hands, feet, nails, groin, and areas other.
Athlete's foot is caused by the ringworm fungus ("tinea" in medical jargon). Athlete's foot is also called tinea pedis. The fungus that causes athlete's foot can be found in many locations, including floors in gyms, locker rooms clothes (locker rooms), swimming pools, nail salons, and in socks and underwear. Mushrooms can also be spread directly from person to person or by touch (contact) with these objects.
However, without the growing conditions are right (an environment that is warm and humid), the fungus may not easily infect the skin. Up to 70% of the population may have athlete's foot at some point during their lives. Symptoms of Athlete's Foot
Symptoms of Athlete's Foot
The symptoms of athlete's foot typically include varying degrees of itching and burning. The skin may frequently peel, and in cases of particularly severe, there may be some cracking, pain and bleeding as well. Some people have no symptoms at all and did not know they have an infection.
Form Athlete's Foot
Athlete's foot may appear as areas of red skin, peeling and dry in one or both feet. Sometimes dry flakes may spread on the sides and top of the legs. The most common rash is localized on only the soles of the feet. The spaces between the toes of the fourth and fifth also may have some moisture, stripping, and dry flakes. There are three common types of athlete's foot:
There are three common types of athlete's foot:
1. soles of the feet, also called type "moccasin"2. between the toes, also called type "interdigital"3. inflammatory type or blistering (blistering)
The cases that are not public might look like bubbles (blisters) are small or large feet (called bullous tinea pedis), thick patches of red and dry skin, or calluses with redness. Occasionally, it may seem like just a mild, dry skin without the redness or inflammation.
Athlete's foot may present as a rash on one or both legs, and even involving the hands. This is a very common designation of athlete's foot. Fungal infections are called tinea manuum hand. The exact cause of why the infection usually affects only one hand is not known.
Athlete's foot may also be seen along with ringworm of the groin (especially in men) or the hands. It is useful to examine the legs whenever there is a fungal groin rash called tinea cruris. It is important to treat all areas of fungal infection at the same time to avoid re-infection. Are Athlete's Foot Contagious?
Are Athlete's Foot Contagious?
Athlete's foot may spread from person to person, but he did not always contagious. Some people may be more susceptible to the fungus that causes athlete's foot where others are more resistant (resistant). There are many households where two people (often husband and wife or children) who use the same bathing place for many years the fungus has not spread among them. The exact cause of this tendency or susceptibility to fungal infections is unknown. Some people seem more prone to fungal skin infections than others.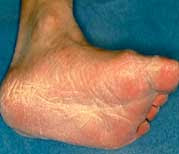 What are the Causes of Rash-Rash Legs?
What are the Causes of Rash-Rash Legs?
There are many possible causes of leg rashes. Athlete's foot is one of the causes are more common. Additional causes include infections of the skin (dermatitis) that irritate or contact (touching), allergic rashes from shoes or other creams, dyshidrotic eczema (allergic skin rash), psoriasis, keratodermia blenorrhagicum, yeast infections, and bacterial infections.
Your doctor can perform a simple test called a KOH, or potassium hydroxide for microscopic examination of fungi, in the office or laboratory to confirm the presence of a fungal infection. This test is carried out by using small pieces of skin were tested under a microscope. Many skin specialists (dermatologists) to conduct this test in their practice with results available within minutes. Rarely, a small piece of skin may be removed and sent for biopsy to help confirm the diagnosis. Athlete's Foot Care
Athlete's Foot Care
Treatment athlete's foot can be divided into two parts. The first, and most important part, is to make the infected area less suitable for athlete's foot fungus to grow. This means keeping the area clean and dry.
Buy shoes that are leather or other material that can breathe. Shoe materials, like vinyl, which does not breathe cause your legs remain moist, providing an excellent area for mushroom breeding. Likewise, socks that can absorb like cotton which absorbs water from your legs may help.
Powders, especially powders of treatment (such as with miconazole or tolnaftate), can help keep your feet dry. Finally, your feet can be soaked in a solution of dry aluminum acetate (Burrow's solution or solution Domeboro). A home-made drugs from the marinade of white vinegar diluted using one part vinegar and about four parts water, once or twice per day as a bath-soaking feet for 10 minutes may be helpful in treatment.
The second part of the treatment is the use of creams and anti-fungal rinse-rinse. Many medications are available, including sprays and creams miconazole, clotrimazole, terbinafine (Lamisil), and ketoconazole shampoo and cream, and so on. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a recommendation. Treatment for athlete's foot should generally be continued for four weeks, or at least one week after all symptoms of the skin has been lost.
The cases are more advanced or resistant of athlete's foot may require a trip of two to three weeks of an antifungal oral (pill) such as terbinafine, itraconazole (Sporanox) or fluconazole (Diflucan). Laboratory blood tests to make sure no liver disease may be necessary before taking these pills.
Topical corticosteroid creams (worn on the outside) can work as a fertilizer for mushrooms and may actually worsen skin fungal infections. These medications are topical steroids have no role in treating athlete's foot.
If the fungal infection has spread to the nails of the toes, the nails should also be treated to avoid re-infection of the feet. Often, the nails were initially ignored only to find the athlete's foot remained relapse. It is important to take care of all the mushrooms that look at the same time. Effective nail fungus treatment is more intensive and may require prolonged journeys (three to four months) of anti-fungal medications orally. When should I seek medical care?
When should I seek medical care?
If you notice any redness, increased swelling, bleeding, or if your infection does not disappear, see your doctor. If a bacterial infection also occurs, an antibiotic pills may be necessary. If you have a fungal nail involvement, are diabetic, or have a compromised immune system, you should also visit your doctor immediately for treatment. Possible Complications of Athlete's Foot
Possible Complications of Athlete's Foot
Not treated, athlete's foot can potentially spread to other body parts or other persons including family members. Fungus may spread locally to the legs, toe nails, hands, finger nails, and basically any body area.
This type of fungus is generally happy to live in the skin, hair, and nails. He did not attack the inside, go to the organs of the body, or go into the blood system.
Fungal infections of the nails is called tinea unguium or onychomycosis. Nail fungus is probably very difficult to treat. Antifungal pills may be necessary in cases of further infections toe nail fungus.
People with diabetes, HIV / AIDS, cancer, or other immune problems may be more prone to all kinds of infections, including fungi.
When skin is injured by the fungus, which protects the natural skin barrier broken. Bacteria and yeast, the yeast can then invade the broken skin. Bacteria can cause a foul odor. Bacterial infections of the skin and inflammation that result from it are known as cellulitis. This is especially more likely to occur in older people, individuals with diabetes, chronic leg swelling, or who have been issued vein-vein (such as for heart bypass surgery). Bacterial skin infections also occurred more frequently in patients with immune systems are impaired.
Which type of Doctor Treating Athlete's Foot
Experts in the skin (Dermatologists) specializing in the treatment of skin disorders, including athlete's foot. You may find a list of expert-certified dermatologists in http://www.aad.org. In addition, family medical doctors, internal medical doctors, doctors of children, podiatrists (foot doctors), and other doctors may also treat this common infection. How Do I Prevent Future Infections?
How Do I Prevent Future Infections?
Because some people are simply more susceptible to fungal infections, they are also more susceptible to repeated infections. Preventive measures include maintaining your legs clean and dry, moist environments avoiding prolonged, leave shoe-leather shoes and allow feet to breathe, avoiding the street barefoot, especially in public areas such as swimming pools and gyms, avoid contact with people known to be infected, and avoid the marinade and use of contaminated equipment in nail salons. Disinfect the old shoes and spray weekly or monthly periodic anti-fungal foot powder (Pedi-Foot Dry Powder) into the shoes can also be helpful.
It is imperative to bring the tools of your own nails, including nail files, nail salon to the public anywhere, unless you know the salon to practice strict sterilization equipment and or use of all supplies of disposables thrown away.
Use cotton socks whenever possible. Avoid roads at airports and public areas with bare feet. Make sure everyone from family members are affected as well treat their athlete's foot at the same time to avoid cross infections.
Friday, April 27, 2012
Athlete's Foot - Infections, Care, Contagious, Definition and Treatments (Skin)
Neck Pain - Causes and Informations
Neck Pain - Causes and Information
Summary
Neck pain (neck pain) is a symptom caused by the pressure (stress) on the soft tissues, bones, or joints of the cervical spine (cervical spine) or adjacent structures. In some cases, neck pain may nevertheless result of underlying diseases on the neck or other parts of the body.
The neck is an area of the spine (spine) are the most flexible. It also supports (supporting) the weight of the head. However, is sensitive to the stout neck injuries and diseases that potentially produce pain and restrict movement.
Various factors can contribute to neck pain, including poor posture, trauma and degenerative diseases. The sources of pain include the neck of fractures to meningitis to osteoarthritis to polymyalgia rheumatica to whiplash.
In most cases, neck pain can be treated at home using free prescription drugs, heat therapy, cold therapy and rest. However, pain that can not be disappeared in the two weeks requiring a doctor's attention. Prescription medications, physical therapy, maniulasi therapy and other treatments can cure the vast majority of cases involving neck pain. In rare cases, surgery may be needed. About Neck Pain
About Neck Pain
Neck pain is a common medical condition that can result from many types of stress. Poor posture, accidents, injuries and degenerative diseases may all responsible for causing pain in the neck of a person. In other cases, underlying diseases, such as fibromyalgia, may cause neck pain. Rarely, infection cover the brain can cause neck pain.
The neck is composed of seven bones called vertebrae which begin in the upper torso and end at the base of the skull. Other features of the neck including muscles, tendons, ligaments, facet joints, nerves and discs (discs) intervetebral that absorbs the shock that separates the vertebrae.
Vertebrae of the cervical spine in the neck up. The bony vertebrae and the ligaments of the neck provide stability to the spine, and muscles to allow support (buffering) and movement. Nerves in the neck also spread down into the arms.
The neck allows a greater degree of movement and the head, which can weigh up to 10 pounds (4.5 kilograms). However, the neck is also sensitive to many injuries and diseases potentially resulting in pain and limit range of motion.
In most cases, neck pain disappear with minimal maintenance for a period of weeks. However, some forms of neck pain require professional medical care, including prescription drugs, physical therapy and other treatments. In these cases the most extreme, surgery may be needed to treat neck pain.
The doctor should be contacted immediately if the neck pain associated with any of the following:
Severe pain caused by injury. Patients should always seek medical care after head or neck trauma such as whiplash or a blow on the head. Significant pain over the bone might indicate a fracture or injury to the ligaments. Shooting pain. Pain radiating from the shoulder and continuing through the shoulder blades or down the arm may indicate impact or nerve irritation. Numbness or tingling in the fingers also may indicate that irritation. Nerve irritation can last from three to six months or longer. Chest pain that radiates (spreads) to the neck, arm or jaw may be caused by a heart attack.
Shooting pain. Pain radiating from the shoulder and continuing through the shoulder blades or down the arm may indicate impact or nerve irritation. Numbness or tingling in the fingers also may indicate that irritation. Nerve irritation can last from three to six months or longer. Chest pain that radiates (spreads) to the neck, arm or jaw may be caused by a heart attack.
Loss of strength. Weakness in the arm or leg (often evident when a sudden drop items, or walking with stiff legs or stagger) indicates the need for immediate evaluation.
Changes in the habits of urinating and defecating. Significant changes that may indicate a neurological problem. This is especially true of incontinence (inability to control the disposal of urine and feces).
Area-Area Other Related Pain In Neck Pain
In some cases, neck pain is probably the result of illness or injury to other parts of the body. Areas of the body that can affect the neck include the jaw, head and shoulders.
The conditions that cause pain in the neck and spread to other parts of the body including:
Headaches. Especially tension headaches can cause neck pain. Neck pain may remain alive after a migraine.
Radiculopathy. Pinched nerve, often resulting from a rupture disc (herniated disc). In addition to neck pain, patients may experience pain down the arm that is often described as feeling electrically (electric shock).
Spinal stenosis. The narrowing of the openings around the spinal nerves (spinal cord) or nerve roots. The symptoms mimic those of a pinched nerve.
Spinal instability. Increased movement of the vertebrae that can cause tingling in the neck.
Facet joint arthropathy. Facet joint arthropathy (joint disease) usually occurs with whiplash or other neck injuries anything and can cause pain in the neck and headaches associated posterior.
There are also other conditions where the pain originated in other parts of the body and spreads to the neck, such as TMJ disease. Temporomandibular joint is dependent on the skull where the jaw. Diseases that affect these joints can cause neck pain. In some cases, neck pain can also trigger TMJ pain.
In addition to dental pain, headaches and back pain, neck pain can also be connected to several types of ear pain (eg, malignant external otitis), orofacial pain (eg carotodynia) or shoulder pain. Potential causes for Neck Pain
Potential causes for Neck Pain
Neck pain can result from injuries (or abnormalities within) soft tissues, including muscles, ligaments, intervertebral discs and the nerves, or bones and joints of the spine ( spine).
The neck is sensitive to pain for several reasons. The neck is designed to allow a broad restriction of movement. The beneficial aspects of the design of this neck is also the greatest sensitivity for interconnect structures of the neck exposed to damage from erosion associated with aging, arthritis and excessive stretching by whiplash. The sources of neck pain include:
The sources of neck pain include:
* Muscle tensions. If the neck muscles are used in excess, it may contribute to muscle tension. The muscles in the back of the neck are especially sensitive and can be tightened by daily activities such as long hours of driving or reading in bed. Through time, a recurring tension in these muscles can lead to chronic pain. Lying on a bad posture for long periods of time is a common cause of neck muscle tensions.* Trauma. Because the neck is so flexible and support the weight of the head, he is sensitive to injury. Some injuries, especially those derived from automobile accidents, may result in whiplash, injuries that occur when the head forward and backward. This stretches or tears the soft tissues (like muscles and ligaments) of the neck, resulting in injury and pain. Serious injury can lead to fractures or dislocations of the neck, which may damage the spinal cord and cause paralysis. Also, injury can predispose facet joint arthropathy.* Arthritis. Neck joints tend to deteriorate with age, leading to arthritis. Patients with a history of whiplash is more likely to develop arthritis in the neck as they age. The forms of arthritis in the neck which may cause pain in the neck or elsewhere include:o Osteoarthritis. People occurs in older people caused by the erosion (consumption) of the joints between the bones of the neck. This causes the pain spread to the shoulder or between the shoulder blades. Pain is generally present at the beginning of the day, subsided during the day and then back again at the end of the day.o Rheumatoid arthritis. Chronic disease characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the joints, weakness, loss of mobility (movement) and deformity (deformity). He can cause the destruction of the joints of the neck.o Ankylosing spondylitis. This type of arthritis that primarily affects the spine. Typically it starts in the lower back but can progress to the upper back and neck.* Disease-disc disease. Just as the problems with the lumbar spine and thoracic spine can cause back pain, problems with the cervical spine can cause neck pain:o pinched nerve. When a person ages, the intervertebral discs which serve as cushions between the vertebrae of the spine begins to dry. This narrow spaces in the spinal column where the nerves come out, and put pressure on the spinal nerves.o degenerative disc disease. Discs deteriorate and press upon the nerves.o a rupture disc (Herniated disc). Intervertebral discs sometimes tear or rupture, which means a gelatinous center (such as agar-agar) protruding through a layer of solid discs.* Cervical stenosis. The narrowing of the spinal canal that pinning the bone marrow. When a person ages, the intervertebral discs begin to dry up, reducing their role as a shock absorber-absorber to protect the spinal cord (spinal cord). Degenerative changes in the vertebrae can also foster the growth of bone spurs are pressing the nerve roots. Finally, the bones and ligaments in the spine gradually thicken and become less flexible. All of these changes narrow the spinal canal. The symptoms associated with cervical stenosis include neck pain, numbness and weakness of the hands, inability to walk quickly, deterioration of motor skills are refined and muscle spasms in the legs.* Meningitis. Neck pain associated with headache and fever may be a sign of meningitis, an infection of the membranes surrounding the brain. Extreme stiffness in the neck that are difficult or impossible to touch your chin to the chest may be a sign of meningitis and requires prompt medical attention.* Encephalitis. Inflammation of the brain. Symptoms can include stiffness or back pain or neck.* Fibromyalgia. Chronic disease characterized by musculoskeletal aches, pain and stiffness, the sensitivity of soft tissues, fatigue and sleep disturbances. Neck pain is among the symptoms commonly associated with fibromyalgia.* Myofascial pain syndrome. Chronic musculoskeletal conditions are often associated with trauma, poor posture, sitting at a computer or doing repetitive tasks associated with a person's job. Patients often report feeling pain in various parts of the body including the neck and may have trouble sleeping or feel the break even sleep.* Polymyalgia rheumatica. Inflammatory condition typified by pain and stiffness in the neck, shoulders and hips.* Myositis. Group of conditions that inflamed muscle. Myositis typically overwrite areas near the trunk (torso), such as the neck, shoulders and hips.* Osteoporosis. Bone-thinning disease most common in women during and after menopause. There are no symptoms in early stages, but in later stages osteoporosis can cause fractures of the spine may cause back pain or neck.* Paget's Disease. Metabolic bone disease that involves bone destruction and regrowth that causes deformity (deformity). The cause of this disease is unknown, but it often results in neck pain.* Breast-large and heavy breasts. Women with large breasts often experience pain in your upper neck, which is usually caused by increased pressure on the muscles. Some choose to get surgery to reduce the size of the breasts and relieve neck pain, shoulder and back.* Other conditions. In rare cases, neck pain is the result of other medical illnesses such as cancer, infections or congenital anomalies (birth defects) of the vertebrae. Neck pain can also be a symptom of a heart attack.
The symptoms associated with cervical stenosis include neck pain, numbness and weakness of the hands, inability to walk quickly, deterioration of motor skills are refined and muscle spasms in the legs.* Meningitis. Neck pain associated with headache and fever may be a sign of meningitis, an infection of the membranes surrounding the brain. Extreme stiffness in the neck that are difficult or impossible to touch your chin to the chest may be a sign of meningitis and requires prompt medical attention.* Encephalitis. Inflammation of the brain. Symptoms can include stiffness or back pain or neck.* Fibromyalgia. Chronic disease characterized by musculoskeletal aches, pain and stiffness, the sensitivity of soft tissues, fatigue and sleep disturbances. Neck pain is among the symptoms commonly associated with fibromyalgia.* Myofascial pain syndrome. Chronic musculoskeletal conditions are often associated with trauma, poor posture, sitting at a computer or doing repetitive tasks associated with a person's job. Patients often report feeling pain in various parts of the body including the neck and may have trouble sleeping or feel the break even sleep.* Polymyalgia rheumatica. Inflammatory condition typified by pain and stiffness in the neck, shoulders and hips.* Myositis. Group of conditions that inflamed muscle. Myositis typically overwrite areas near the trunk (torso), such as the neck, shoulders and hips.* Osteoporosis. Bone-thinning disease most common in women during and after menopause. There are no symptoms in early stages, but in later stages osteoporosis can cause fractures of the spine may cause back pain or neck.* Paget's Disease. Metabolic bone disease that involves bone destruction and regrowth that causes deformity (deformity). The cause of this disease is unknown, but it often results in neck pain.* Breast-large and heavy breasts. Women with large breasts often experience pain in your upper neck, which is usually caused by increased pressure on the muscles. Some choose to get surgery to reduce the size of the breasts and relieve neck pain, shoulder and back.* Other conditions. In rare cases, neck pain is the result of other medical illnesses such as cancer, infections or congenital anomalies (birth defects) of the vertebrae. Neck pain can also be a symptom of a heart attack.
Neck pain may also be caused by conditions that cause widespread joint pain, such as Lyme disease, lupus, chronic fatigue syndrome, sickle cell anemia or sarcoidosis. Commercial Tests Do For Neck Pain
Commercial Tests Do For Neck Pain
Patients can often determine many cases of neck pain without having to find a doctor or undergo testing. In most cases, the pain will disappear in a few days or several weeks. If two weeks go by and the levels of pain does not improve, the physician should be consulted.
In diagnosing the source of neck pain, the doctor will review the patient's medical history and perform a physical examination. In some cases, doctors can diagnose the cause of neck pain and recommend treatment based on the answers to the assessment of pain or the questions that are not structured on the type, location and onset of pain. However, there are other events where additional testing may be necessary to make an accurate diagnosis.
These tests often include imaging tests (imaging tests). These techniques may reveal compression (pressure) on the nerve roots, narrowing of the roads out of the nerve roots and spinal cord and disc problems. Examples of techniques used to diagnose neck pain include:
* X-rays. Uncovering the problems in the cervical vertebrae. The types of x-rays include:o myelography. X-ray images of the spinal cord after a dye is injected in the fluid around the spinal cord (spinal cord). This test can reveal if the protruding spinal disc or some other factor swarmed spine nerves and cause pain.o Discography. Special dye is injected into the spinal discs are expected to injured or otherwise damaged. Dye highlighting the damaged areas are expressed as x-rays taken. This procedure is often used in patients who are considering lumbar surgery or the pain has not responded to conventional treatments.o DEXA scan. Measurement of bone density is a routine screening test for osteoporosis.* MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). Allow evaluation of the spinal cord and nerve roots.* CAT scan (computed axial tomography). Permit the evaluation of bone and spinal canal.* Radionuclide bone scan or other imaging. The tests that use radioactive tracers-tracers to highlight the internal structure structure.* Electromyography (EMG). Tests that evaluate the electrical activity in nerves and muscles, helps reveal the damage.
In some cases, physicians may refer patients to specialists of the spine (spine), orthopedist or pain specialist if surgery is not an option (choice) or the patient has refused surgery.
Research has shown that MRI or CAT scan may not come across the facet joint arthropathy, and that the most sensitive test to detect it is a diagnostic injections by pain specialists.
Exemption Options For Neck Pain
In most cases, neck pain respond well to efforts to treat patients at home. Drug-free anti-inflammatory prescription medications such as aspirin, ibuprofen or naproxen can help relieve inflammation and pain. Analgesic, analgesics such as acetaminophen relieve pain but does not reduce inflammation.
Ice (cryotherapy) may also help reduce inflammation. He must application for 15 to 20 minutes, with 40 minutes between applications. Ice should not be directly applied to the skin but should be wrapped in a towel, ice packs or other obstacles. Thermal treatments and water (thermotherapy and hydrotherapy) may also be used to relax the muscles of the lesions (eg, a hot compress, heating pad or hot shower). However, in some cases heat can exacerbate inflammation, so it should be used with caution.
If the treatments themselves do not begin to eliminate neck pain within two weeks, prescription drugs or interventions may need medical pain control. This may include:
* Physical therapy. Care where a physical therapist will design and execute therapeutic stretching and strengthening exercises that increase the support structures of the cervical spine. In many cases, such therapy alone is sufficient to relieve neck pain. The therapist may also use modalities (how something is done) such as hot packs, therapeutic ultrasound or electrical therapy to relieve pain and maximize the movement restrictions. Patients can be instructed to use transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) at home.* Therapeutic manipulation. Experts such as chiropractors, osteopaths or massage therapist may offer liberation.* Drug-drug. Prescription pain medications have many of the effects of anti-inflammation and relieve pain the same as prescription drugs are free, but offer them in doses more powerful. However, some are available only by prescription. Examples of these medications include:o Opioids. Prescribed to control acute and chronic pain is severe, these medications should be used only under the strict supervision of physicians, because they can have many side effects, including drowsiness, reduced reaction time, impaired decision, depression and addiction.o Antidepressants. Some antidepressants can relieve pain and aid sleep.* Therapeutic injections. A number of injections, including epidurals, facet joint injections and nerve barriers, are available for patients who do not want surgery. These injections are usually do by pain specialists who are trained in the neck area.* Immobilization (disablement) short-term. A soft neck collar can be worn for a period of time. It supports the spine, reduces mobility and reduce pain and irritation while allowing the neck muscles to relax when they heal.* Traction. Cervical traction tool attached to the head and using weights-weights and pulley (pulley) to pull the head. This framework is designed to attract structure neck into alignment (straightness) the better. He is especially useful in treating nerve root irritation, and pain relief may last for hours or days. Traction may be used in cases of an unstable spine, or vertebral fractures but not commonly done. Other treatment methods that doctors may recommend include cognitive behavioral therapy for chronic neck pain or complementary treatments (complementary) and alternatives such as acupuncture, acupressure, or biofeedback. If noninvasive methods fail, the options (choices) may include:
Other treatment methods that doctors may recommend include cognitive behavioral therapy for chronic neck pain or complementary treatments (complementary) and alternatives such as acupuncture, acupressure, or biofeedback. If noninvasive methods fail, the options (choices) may include:
* Cervical spine surgery. In rare cases, surgery may be necessary to treat neck pain. He is most often used to relieve pressure from nerve roots or spinal cord (spinal cord) caused by a rupture disc (herniated disc) or narrowing of the bones of the spinal canal. Operations also may be needed to stabilize the neck and minimize the possibility of paralysis after injury. Operating options including:o Anterior cervical discectomy. The most common surgical procedure used to relieve neck pain caused by pressure on one or more nerve roots or the spinal cord (spinal cord). This procedure enlarging the opening of nerves and spinal discs issued are troublesome. Bone spurs are pressing bags spine or nerve roots are also excluded.o Cervical corpectomy. A more extensive version of anterior cervical discectomy, it involves the expenditure of the vertebrae and discs. The risks are slightly higher with this procedure and include damage to the nerve roots and spinal cord, bleeding, infection, damage to the trachea or esophagus, and paralysis.o Posterior hemi-laminectomy. The operation is performed through a vertical incision on the back of the neck where the bones around the spinal cord or nerve openings removed. Ligaments that attach the bag to exert pressure on the spine and nerve roots are also excluded.o Spinal fusion. This procedure will reduce the restriction in neck movement.o Verebroplasty or kyphoplasty. These procedures may use for compression fractures caused by steoporosis.
Recent studies suggest that injections of botulinum toxin type A, a popular method of fighting wrinkles, may ease chronic neck pain and other pain conditions ranging from migraines to tennis elbow to back pain.
Treatment by a physician or other health professionals likely to proceed in three phases. Initially, treatment will focus on reducing pain and inflammation. The second phase concentrated on advancing the increased strength and flexibility of networks. The final phase involves the exercise and lifestyle techniques that will help patients maintain strength and flexibility is to minimize the risk of neck pain episodes future.
Prevention Methods For Neck Pain
The main source of neck pain - poor posture - can be easily rectified (corrected). Proper posture involves maintaining the neck in a neutral position with the head backward, so he concentrated on the spine. It works with gravity to keep the neck rather than fight it. Also it is important to avoid menggertakan teeth, which can put strain on the neck muscles. Steps that can be taken to improve posture and ergonomics including:
Steps that can be taken to improve posture and ergonomics including:
* Take breaks often. People who are driving long-distance or working on the computer for hours is likely to suffer from neck muscles are tensed. Taking breaks from these activities can provide opportunities neck muscles to relax.* Sit with right. The chairs and tables in the workplace should be adjusted so that computer monitors are at eye level and the knees slightly lower than the hips. The chairs should also have the hands of the chair. The people who sit for long periods of time in the car to put a small pillow or rolled-up towel between the neck and the headrest. This maintains the natural curve of the neck.* Avoid the phone tucked between ear and shoulder. People who often use the phone must use a headset instead.* Stretch frequently and exercise. The muscles of the neck may be stretched by lift the shoulders (the shoulders) up and down. Also helping to pull shoulder blades together and then relax. Pulling the shoulders down while leaning his head on each side can also stretch the muscles of the neck. Walking causes the spine spins, which provides an excellent workout for the muscles of the neck.* Balancing basis. Stretching the muscles of the chest wall and strengthening the muscles around the automatic shoulder blade and back of the shoulder can promote a balanced base of support for the neck.* Avoid sleeping on the stomach. Sleeping on the stomach to put pressure on the neck. Clear-cushion should be chosen that support the natural curve of the neck.* Do not read in bed. This causes neck strain, especially when propped up on a pillow with the neck bent forward and arms issued to hold the book. People who can not submit a reading in bed pillow wedge should buy or mini table that can be taken that are designed to read in bed.* Keep your weight evenly distributed. Do not carry the goods on one shoulder for too long. If possible, take the items in the backpack, which distributes the weight evenly. However, do not impose too heavy backpack.* Use the techniques of proper lifting. Lift from the knees, not the waist, to protect both the neck and lower back. When lifting heavy objects, keep your back flat and close to the body burden. Do not twist your back when lifting. If heavy or awkward objects, do not lift it without assistance partners.
In addition, neck injuries can be prevented by taking precautionary measures in situations where vulnerability neck. This may include wearing seat belts (safety belts) when driving or riding a motorbike, wear protective equipment when playing sports, and be careful to not dive in shallow waters when swimming.
Questions For Your Doctor Regarding Neck Pain
Prepare questions in advance can help patients have discussions more meaningful with their doctors regarding their conditions. Patients may want to ask the doctor the following questions about neck pain:
1. What can be causing my neck pain?2. What tests may be required to seek the source of neck pain (neck pain) I?3. Involves what these tests? Should I do anything to prepare? Where and when I would have them?4. The results of my tests showed what - what the source of my neck pain?5. Is the neck pain I probably lasted a short or chronic?6. Is it possible that conditions in other parts of my body causing pain in my neck?7. Treatment choices I what?8. If treatments are not invasive did not work, will I need surgery to treat my neck pain?9. How can I keep the neck pain of recurrence?10. Are there exercises and certain activities that I should do or avoid?11. Is there something I can do to prevent neck pain?
Splenomegaly (Enlarged Spleen) - Treatments, Sign, and Symptoms
Splenomegaly (Enlarged Spleen) - Treatments, Sign, and Symptoms
Definition of Spleen distention
Spleen (spleen) is an organ located in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen just below the diaphragm and is protected under the ribs left bottom.
The spleen has several important functions that involve blood cells in the body.
1. He is to filter blood and remove red blood cells are old and damaged, bacteria and other particles as they pass through an intricate network of blood vessels in the spleen.2. He produces lymphocytes, a type of white blood cells that produce antibodies and aid the immune system.
Filtering system is part of the red pulp and white pulp of the spleen while the cells containing the immune function.
Normally, the spleen is a small organ about the size of a small fist or orange. Splenomegaly describe situations in which the spleen enlarges in size. (+ Megaly = enlarged spleen) What are the causes of Spleen distention
What are the causes of Spleen distention
The spleen enlarges if he was asked to do excessive work in the filter or make blood cells, if there is abnormal blood flow to him, or if it was invaded by abnormal cells or deposits.
Red Blood Cells Abnormal: Because the spleen filter out abnormal blood cells and remove them from the circulatory system, diseases that result in abnormal red cells will cause enlarged spleen. Sickle cell disease (Sickle), thalassemia, and spherocytosis are examples of diseases that make up the cells that form unusual that can not easily maneuver through the blood vessels and small capillaries of the body. If they are not removed by the spleen, these abnormal cells can cause blood clots and reduce circulation. However, removing them causes the spleen to swell and enlarge.
Viral and Bacterial Infections: The spleen is involved in the manufacture of cells that fight infection and part of response it is enlarged. It is generally seen in viral infections such as infectious mononucleosis (caused by Epstein Barr virus), AIDS and hepatitis viruses. Examples of bacterial infections associated with splenomegaly includes tuberculosis, malaria, and anaplasmosis (formerly known as ehrlichiosis).
Splenic vein pressure / blockage: Blood enters the spleen through the splenic artery and left through the splenic vein. If the pressure within the veins is higher or if the splenic vein becomes blocked, blood can not leave the spleen and it may swell. Because blood flow relationships in the liver, cirrhosis and portal vein obstruction can cause complications with venous blood flow from the spleen. Congestive heart failure may lead to both liver and spleen to swell because of increased venous pressure. Cancers: leukemia, lymphoma, leukemia and both non-Hodgkins and Hodgkins can cause enlarged spleen, such as the diversity of other tumors including melanoma, melanoma can.
Cancers: leukemia, lymphoma, leukemia and both non-Hodgkins and Hodgkins can cause enlarged spleen, such as the diversity of other tumors including melanoma, melanoma can.
Metabolic Diseases: Metabolic Diseases which enlarge the spleen, including Niemann-Pick disease, Gaucher disease and Hurler's syndrome.
The symptoms of an enlarged spleen
An enlarged spleen itself usually causes no symptoms, the symptoms of the underlying disease is often because the patient may seek treatment. This may include weakness and fatigue from anemia, easy bleeding from decreased platelets in the blood stream, or recurrent infections of white blood cells function poorly.
However, when the spleen enlarges, it can suppress the diaphragm, the muscle that separates the living-room chest and abdomen. Irritation of the diaphragm may refer to left shoulder pain. An enlarged spleen can also push forward the stomach and cause anorexia or loss of appetite and early satiety feeling when time to eat.
Because the spleen is enlarged to grow beyond the protection of the rib cage becomes more likely he is injured, thereby increasing the chance that the abdominal pain may occur.
Depending on the amount of damage to the spleen after injury, can occur with bleeding into the abdominal distension (bloating) associated, in the back and shoulder pain, and signs and symptoms of shock. These can include weakness, shortness of breath, and the skin cold, damp and sweaty. When should I seek medical care for an enlarged spleen?
When should I seek medical care for an enlarged spleen?
Most often, the diagnosis of an enlarged spleen was made by chance by a physician. There are usually no symptoms that would bring a patient seeking a doctor. However, symptoms that can not be explained as mentioned above should be investigated by a doctor.
Spleen Yang diagnose distention
Most often an enlarged spleen discovered incidentally on physical examination by a physician. The spleen is usually small enough to hide under the rib cage to the upper abdomen. The tip of the enlarged spleen may be felt in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen and when he continues to move toward edge enlarged right lower quadrant. In some people who are thin, the spleen may be felt in the abdomen but normal in size. An enlarged spleen measuring approximately 12 to 20 cm (4.5 to 8 inches) in any dimension while the spleen is larger than 20 cm (8 inches) are considered as severe enlargement.
If there is concern that the enlarged spleen, blood tests may be considered to assess the cause of enlargement. Common tests may include complete blood cell count (CBC) seeking virgin cells are abnormal red and white, peripheral smear to assess the types and forms of blood cells or monospot, if the diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis is taken into consideration. Other tests that evaluate liver function and heart may be considered if clinically indicated.
Abdominal ultrasound, CT, or MRI of the abdomen may be used to evaluate the size of the spleen and to look for other abnormalities in the abdominal cavity that may be associated with splenomegaly. Treatment For Spleen Yang distention
Treatment For Spleen Yang distention
Treatment for an enlarged spleen is usually directed at the underlying medical conditions that result in splenomegaly. Depending on the underlying issues, treatments can occur with antibiotic, chemotherapy, or radiation. These treatments are for the underlying disease and may allow for reduced spleen size ; however, in some cases, will remain enlarged spleen.
Occasionally, the spleen may need to be surgically removed (splenectomy + = spleen ectomy = expenditure) as part of treatment disease. For example, the inherited spherocytosis, spleen expenditure happen prevent anemia when red blood cells are abnormally shaped continuously filtered out and removed from the bloodstream. What are the complications of an enlarged spleen
What are the complications of an enlarged spleen
When the spleen enlarges, it loses some of its patron from the bottom of the rib cage and become more susceptible to injury. The enlarged spleen is fragile and can be damaged by the blows that are relatively minor in the upper abdomen. He is a relatively solid organ and can crack causing life-threatening bleeding and potentially significant. An enlarged spleen may also ensnare the number of blood cells in it that causes excessive:
An enlarged spleen may also ensnare the number of blood cells in it that causes excessive:
* Anemia (number of red blood-cell count is reduced), which may lead to weakness, shortness of breath, and fatigue;* Leukopenia (white blood cells is reduced), which may lead to an increased risk of infection; and* Thrombocytopenia (reduced platelets), which may lead to infection or bleeding problems.
If the spleen is necessary to issue, there is an increased risk of infection, mainly caused by bacteria such as pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae), Hemophilus influenza, and meningococcus (Neisseria meningitides). It is important to consider the maintenance of immunization, current immunization (particularly pneumococcal vaccine, because about 50% to 90% of infections after splenectomy caused by encapsulated streptococci) against infkesi-infection in patients who had spleen removed. Spleen prevent distention
Spleen prevent distention
Splenomegaly is a complication of underlying disease, and he himself can not be prevented. Ideally, early recognition of an enlarged spleen may help doctors come up to the early diagnosis of the cause and may prevent further enlargement of the spleen.The prognosis (forecast) for Spleen Yang distention
Depending on the cause, the enlarged spleen may return to normal size and function if the underlying disease being treated and eliminated.
* Usually, in infectious mononucleosis, the spleen returned to normal when the infection improved.* In some circumstances, removing the spleen is part of the treatment and can make the person more susceptible to an infection-infection.* Many diseases result in an enlarged spleen as a permanent physical findings and may result in only a fair prognosis because that person might be in-creased spleen injuries, infections, and abnormal bleeding.
Lymph (Node Swelling) - Inflammation, Infections
Lymph (Node Swelling) - Inflammation, Infections

Definition of lymph node
Lymph node-is an important component of the body's immune system and helps in fighting infections.
They are the structures are small, soft, round or oval are found throughout the body and relate to each other in chain-like model (lymphatic chains) by canals similar to blood vessels. Each individual lymph nodes enveloped by a capsule formed from connective tissue.
Inside the capsule, lymph node-containing certain types of immune cells. These cells are predominantly lymphocytes, which produce proteins that capture and combat viruses and other microbes, and macrophages, which destroy and remove the captured material.
Locations lymph node
Lymph node-located throughout the body. Some are directly under the skin where the others are in the body. Lymph node-even the most superficial (close to the skin) is usually not visible or palpable (felt by touch), unless they are swollen or enlarged to some causes.
They are connected to each other by the lymphatic vessels are bound to loose. Lymph node, usually joined at the different areas inside the body where they are responsible for filtering the blood and carry out their immunological function for that particular area of the body. Fluid of the lymphatic vessels into the venous system eventually (the veins) in the body.
Causes of Swollen lymph nodes
There is ample causes for node-swollen lymph nodes, sometimes referred to as "swollen glands" or "swollen glands" (lymphadenopathy or lymphadenitis). In general, lymph, lymph nodes swell when they actively caused by an infection, inflammation, or cancer. Infections
Infections
Infections are the causes of the most common of the node, swollen lymph nodes. Infectious causes of the common-node swollen lymph node is a virus, bacteria, parasites, and fungi.
Viruses
* Infectious mononucleosis (mono),* Chickenpox,* Measles,* HIV,* Herpes,* Common cold viruses,* Adenovirus, and* Many other viruses
Bacteria
* Streptococcus,* Staphylococcus,* Cat scratch disease,* Syphilis,* Tuberculosis,* Chlamydia, and* Other sexual diseases are transmitted
Parasites
* Toxoplasmosis,* Leshmaniasis
Mushrooms:
* Coccidiomycosis,* Histoplamosis
Inflammation
Causes are inflammation and imunoligik of node-swollen lymph node includes diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus as well as sensitivity to some drugs.
Cancer
Corpulent cancers can also cause swelling of lymph-node. This is probably the cancers that originate from the lymph-lymph nodes or blood cells such as lymphomas and leukemias. They may also be cancer-that spread from other organs in the body (metastatic cancers). For example, breast cancer may spread to the lymph, lymph node nearest the axilla (under arm), or lung cancer may spread to the lymph, lymph nodes around the collarbone.
Other causes of Swollen lymph nodes
There are other causes are less common than lymph-node swelling, such as genetic diseases of lipid storage (genetic lipid storage diseases), transplant rejection, graft rejection (transplant graft rejections), sarcoidosis, and many other conditions.
It is also important to mention that the node-swollen lymph node is not always a sign of an underlying disease. Sometimes they can be normal. For example, lymph node, small (less than 1 centimeter), and flat under the jaw (submandibular lymph nodes) in healthy children and young adults lymph nodes or lymph-groin (inguinal lymph nodes) is small (up to with 2 centimeters) in young individuals may be normal.
In many instances, a definitive cause for the node-swollen lymph node may not be determined even after conducting a thorough examination and testing. Symptoms Swollen lymph nodes
Symptoms Swollen lymph nodes
The symptoms from the nodes, swollen lymph nodes varies widely. A person can be completely free of symptoms (asymptomatic) and only found when they were recorded by a doctor during a general physical examination.
Occasionally, nodes, swollen lymph nodes may become very sensitive, painful, and vilify.
More importantly, other symptoms associated with an underlying disease that accompany swelling of the lymph node may be more significant and clinically relevant than the lymph node swelling alone. For example, symptoms such as fever, night sweats, weight loss, or evidence of local infections (toothache, sore throat) may provide valuable clues in determining the cause of swelling of the lymph node.
Diagnosing Swollen lymph nodes
Nodes-the swollen lymph nodes that are closer to the surface of the body is generally diagnosed by a doctor's examination and feel the areas that are known to have a federation of node-lymph node, for example, node-swollen lymph nodes under the arms (axillary lymph nodes) , node-swollen lymph node on the sides of the neck (cervical lymph nodes), or node, lymph node swelling in the groin (inguinal lymph nodes). Swollen lymph-nodes that can be easily seen and felt.
Other times, lymph, lymph node deeper can be seen on imaging studies, such as CT scan (computed tomography), from the body parts are different.
Tonsil-tonsils behind the throat are also lymph-lymph node, and they are one of the most visible in the body.
Diagnosing the cause of node-swollen lymph node may be challenging at times. The most important component of evaluating lymph node swelling is a whole medical history and a complete physical examination by a physician. Your doctor may ask you about your symptoms such as sore throat, fever and chills, fatigue, weight loss, a complete list of drugs, sexual activity, history of vaccination, the trips recently, the history of the patient's cancer himself and his family, if any, and so on.
A group of nodes, lymph nodes in a particular area of the body reacts to the disturbances in that general area. If there is a specific infection in the area of the swollen lymph node, it is probably the most likely cause of the swelling. For example, an infection of the feet or a few diseases that are transmitted sexually can cause swelling of the lymph, lymph nodes in the groin area.
Doctors usually test the lymph node-by feeling them and classify them based on what it's like-lymph node. They can be classified, for example, as:
* Large or small,* Sensitive or insensitive,* Settling or moving (mobile),* Hard or soft, or* Solid or elastic.
These characteristics can be useful in suggesting the cause of swelling of the lymph node. For example, a lymph node is hard, insensitive, no move is probably more characteristic of a cancer that spreads to the lymph it. On the other hand, a lymph node that soft, sensitive, able to move can be more likely to represent an infection.
If the enlarged lymph nodes associated with a cancer is suspected, then a biopsy of the lymph node may determine the type of cancer. For example, a lymph node swelling around the collarbone (supraclavicular lymph nodes), may indicate lung cancer in someone who may have other clinical clues that suggest lung cancer. Treating Swollen lymph nodes
Treating Swollen lymph nodes
There is no specific treatment for node-swollen lymph node. Generally, the underlying cause needs to be treated, which may result in resolution of a swollen lymph node.
Treating an infection that causes swelling of the lymph node, for example, will result in the lymph node swelling which will subside. If lymph nodes are swollen due to a cancer of the lymph nodes (lymphoma), then the swelling will recede after treatment of lymphoma.
When I should be visiting the doctor for swollen lymph nodes?
If the swollen lymph nodes, associated with fevers, night sweats, or weight loss, and patients do not have any real infection, he may need a thorough evaluation by a physician.
Also, people who have been treated appropriately for an infection but have swollen lymph nodes-which persistent / persistent may need to visit a doctor.
If a patient has a cancer known, or been treated for a past and he note lymph nodes-new in the general area of cancer, she may need to tell a doctor.
Lymph-nodes may swell lymph Commercial
There are many lymph node-adults in various parts of the body may swell for different reasons. Many people can usually view-node swollen lymph nodes in the neck, behind ears, under the jaw, above the clavicle (collar bone), under the arms, and around the groin.
Node-swollen lymph node on the side of the neck or under the jaw is the most common. They may represent an infection around the area, such as a tooth infection or ulcers, throat infections, viral diseases, or upper respiratory tract infections. Most of the cause-node-Causes of swollen lymph nodes in this area is not dangerous; however, occasionally, swelling of the lymph, lymph nodes may also suggest a cancer in the head and neck area.
Nodes-the swollen lymph nodes behind the ear may be associated with an infection around the scalp or the possibility of a conjunctival (eye) infection.
Lymph-lymph node under the arm (axilla) is anatomically important in breast cancer. They are often physically tested in patients who underwent screening for breast cancer. They also play an important role in the pen-stadium (determining the extent) and predict outcome of breast cancer during the removal of tissue from breast cancer. Lymph-node can also be reactive and enlarged due to a trauma or an infection of the arm on the same side.
Node-enlarged lymph nodes above the collarbone (supraclavicular lymphadenopathy) are always considered abnormal. It generally suggests a cancer or an infection from an adjacent area. Examples of this might include lung infections, lung cancer, lymphoma in the chest cavity, or breast cancer. Sometimes cancers that may sow the seeds of further lymph-lymph nodes, such as genital cancers or colon cancer. Some of the causes that are not dangerous from the node-swollen lymph nodes above the collarbone (clavicle) can include tuberculosis or sarcoidosis.
Nodes-the swollen lymph nodes in the groin may be normal in young people as it is called early. However, they can also result from several diseases that are transmitted sexually, genital cancers, or infections of the feet on the same side.
What are the complications Swollen lymph nodes
Maybe there are some complications associated with the node-enlarged lymph node. If the swelling of lymph nodes associated with an untreated infection, an abscess (a cavity containing pus) may occur, which may require drainage through the incision and antibiotics. The skin underlying the enlarged lymph nodes may also become infected.
In other cases, the lymph nodes may become very large and suppress other structures adjacent to the body. This can be a serious and horrible problem that may require medical attention or surgery immediately. For example, the lymph nodes under the arm (axilla) can suppress the blood vessels and nerves that supply the arm. An enlarged lymph node in the stomach may push the intestines and cause an obstruction / hindrance of the intestines.
Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar) - Sign Symptoms Causes
Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar) - Sign Symptoms Causes Definition of Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)
Definition of Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)
Hypoglycemia is a clinical syndrome resulting from low blood sugar. The symptoms of hypoglycemia can vary from person to person, as can also severity. Classically, hypoglycemia is diagnosed with low blood sugar with symptoms that disappear when the sugar level back to normal range.
Who Is At Risk for Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)?
While patients who did not have metabolic problems can complain of any symptoms of low blood sugar suggest, correct hypoglycemia usually occurs in patients being treated for diabetes (type 1 and type 2). Patients with pre-diabetes who have insulin resistance may also sometimes have low blood sugars when their levels of circulating insulin further challenged by a prolonged period of fasting. There are other causes are rare for hypoglycemia, such as tumors produce insulin (insulinomas) and certain medications. The causes of this unusual hypoglycemia will not be discussed in this article, which will mainly focus on the hypoglycemia that occurs with diabetes mellitus and its treatment.
Even with our advances in treating diabetes, hypoglycemic episodes are often the limiting factor in achieving optimal blood sugar control. In large scale studies that pay attention to strict control in both type 1 and type 2, low blood sugars occurred more frequently in patients who controlled most intensive. It is important for patients and doctors to recognize it, especially as the goal for treating patients with diabetes be-Asien blood sugar control is more stringent. I Think High Blood Sugar Is Bad. Why Low Blood Sugar Also Bad?
I Think High Blood Sugar Is Bad. Why Low Blood Sugar Also Bad?
The body needs fuel to work. One of the sources of fuel are the main sugars, obtained the body of what is consumed as simple sugars or complex carbohydrates. For emergency situations (such as prolonged fasting), the body stores sugar as glycogen in the liver. If supplies are needed, the body running a biochemical process called gluco-neo-genesis (which means to "create a new sugar") and change these provisions, supplies of glycogen into sugar. Provisioning process is emphasized that the fuel source from sugar is important (important enough for humans to have developed an evolutionary storage system to avoid the dryness of sugar).
Of all the organs in the body, the brain depends on sugar (which we will now refer to as glucose) almost exclusively. Rarely, if really necessary, the brain will use ketone as a fuel source, but it was not preferred. The brain can not make glucose own and is dependent on the entire body to supply. If for some reason, the level of glucose in the blood falls (or if the purposes of the brain increases and the demands are not met) can occur effects on brain function.
Body Can Protect Himself From Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)?
When the level of circulating blood glucose falls, the brain actually feel the fall. The brain then sends out messages that trigger a series of events, including changes in hormones and the nervous system responses aimed at increasing blood glucose levels. Expenditure reduced insulin and hormones that promote blood glucose levels are higher, such as glucagon, cortisol, growth hormone, and epinephrine are all increased. As mentioned above, there are supplies of glycogen in the liver that can be quickly converted into glucose.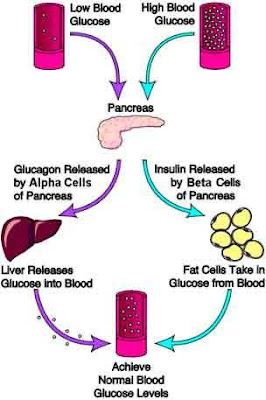 In addition to the biochemical processes that occur, the body begins to consciously alert the affected person that an inter food by causing the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia are discussed below.Symptoms of Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar), and How Low Is Too Low?
In addition to the biochemical processes that occur, the body begins to consciously alert the affected person that an inter food by causing the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia are discussed below.Symptoms of Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar), and How Low Is Too Low?
Biochemical response of the body in hypoglycemia usually starts when sugars are at a height / mid of 70s. At this point, the liver releases his supply and supplies, the hormones mentioned above began to indulge. In many people, this process occurs without any clinical symptoms. The amount of insulin produced is also low in an attempt to prevent a further fall in glucose.
While there is some degree of diversity among the people, most will usually develop symptoms that suggest hypoglycemia when blood glucose levels down to the mid 60s. The first set of symptoms called adrenergic (or sympathetic) because they relate to the nervous system response to hypoglycemia. Patients may experience any of the following;
* Anxiety,* Sweating,* A great hunger,* Chills,* Weakness,* Palpitations, and* Often has difficulty speaking. In most patients, these symptoms are easily recognizable. The vast majority of patients with only experienced this degree of hypoglycemia if they are on drugs or insulin. Patients (with diabetes or who have insulin resistance) with high levels of circulating insulin are fasting or reduce their carbohydrate intake drastically should also commemorated. These individuals may also individual experience hypoglycemia being.
In most patients, these symptoms are easily recognizable. The vast majority of patients with only experienced this degree of hypoglycemia if they are on drugs or insulin. Patients (with diabetes or who have insulin resistance) with high levels of circulating insulin are fasting or reduce their carbohydrate intake drastically should also commemorated. These individuals may also individual experience hypoglycemia being.
Anyone who has experienced episodes of hypoglycemia describe the sense of emergency to eat and relieve symptoms. And, it just is the essence of these symptoms. They act as warning signs. At this level, the brain is still able to access the circulating blood glucose for fuel. The symptoms of a person providing an opportunity to raise blood glucose levels before the brain is affected.
If someone does not or can not respond by eating something to raise blood glucose, the levels of glucose continues to fall. At one place on the limits of 50 mg / dl, most patients continued into the limitations neuro-glyco-penic (brain not getting enough glucose). In this time, the symptoms progress to confusion, sleepiness, changes in behavior, coma, and seizures (attacks).
Treating Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)
Control of acute hypoglycemia involving shipping / delivery is faster than the source of sugars that are easily absorbed. Regular soda, juice, lifesavers, table sugar, and the like are good options. In general, doses of 15 grams of glucose is given, followed by assessment of symptoms and blood glucose check if possible. Jia after 10 minutes there is no improvement, an additional 10-15 grams should be given. This can be repeated up to three times. At that point, the patient should be considered as not responding to therapy and ambulance should be called.
Ekwivalensi than 10-15 grams of glucose is:
* Four lifesavers* 4 teaspoons sugar* 1 / 2 can of regular soda or juice
Many people like the idea of treating hypoglycemia with cake, cookies, and brownies. However, sugar in the form of complex carbohydrates or sugars combined with fats and proteins is far too slowly absorbed to be beneficial in the acute treatment of hypoglycemia.
Once the acute episode has been treated, healthy carbohydrates and long acting to maintain blood sugars at the appropriate boundaries should be consumed. Half a sandwich is a viable option.
If a hypoglycemic episode has progressed to the point where the patient can not or will not eat anything by mouth, which measures more drastic will be necessary. In many cases, family members or roommates can be trained in the use of glucagon. Glucagon causes the rapid release of glucose deposits from the heart. He was given intramuscular injections in patients who can not eat glucose by mouth. Response is usually seen within minutes and lasts for approximately 90 minutes. Once again, a long acting source of glucose must be consumed afterward to maintain blood sugar levels within safe limits. If glucagon is not available and the patient is unable to eat anything by mouth, emergency services (eg 911) must be called immediately. Intravenous routes of glucose entry should be established as soon as possible.
With a history of recurrent hypoglycemic episodes, the first step in treatment is to assess whether the hypoglycemia associated with drugs or insulin treatment. Patients with a consistent pattern of hypoglycemia may benefit from the adjustment of drug dosage. It is important that patients check the values of blood glucose several times a day to help determine whether there is a pattern related to foods or medications.Again, What To Do To Control Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)?
Yes. Patients must wear identification stating that they had diabetes and whether they have a recurrence of hypoglycemia. Patients at risk for hypoglycemia should be advised to check blood sugars before they drive a car, running heavy machinery, or do anything that imposes a physical. In addition, patients should bring fast acting source of glucose (as mentioned above) at any time, and save the source in the car, office, and next to their beds. Efforts should be made to shrink the hypoglycemic effects of regimen-drug regimens and avoid diversity jolt-jolt on the exercise, activity and consumption of alcohol.